Overview
There are several terms and concepts that are unique to Hyperledger Fabric which Fabric DevKit is based. Please refer to the official documentation for a detailed explanation of the terms used. For the purpose of Fabric DevKit, we summarised some of the key terms used and these are:
| Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| Chaincode | A Go, Node or Hyperledger Fabric support code installed on peer node to enable it to perform computation |
| Channel | A subnet of a Fabric network. |
| Client node | A type of node serving as an interface between a human user and a peer node |
| Fabric network | A network of a grouping of client, peer and ordering nodes. Each grouping is typically owned by a participant |
| Fabric Organisation (or Organisation) | A grouping of nodes identified by a root domain with each node in the grouping identified by sub-domain |
| Ledger | A series of timed transactions recorded in blocks that are cryptographically linked. |
| Node | A node a generalised term for computing platform responsible for processing blockchain ledgers, handling interactions with human users and enabling the blockchain network to reach consensus. |
| Participant | This refer to an entity typically an real world organisation or even a individual owning a collection of computing nodes |
| Peer node | A type of node responsible for validating transactions sent from client nodes. |
| Ordering node | A type of node responsible for taking transactions of a client node and packing it into a block and sending the block to the peer node to update the world state. |
| World state | A world state is datastore found in peer nodes representing the state generated from the clumination of transactions found in the ledger. All peers in the same channel share the same state or data structure and should have the same value for a given time frame – i.e. consensus view. |
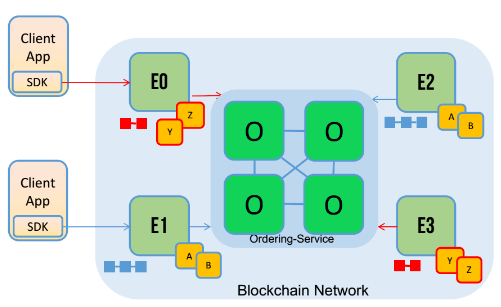
NOTE: In the above diagram, the red and blue ledger notations represents different channels of a given Fabric Network. E0. E1, E2 and E3 represents peer nodes.
Key concepts from official documentation
- Introduction.
- Hyperledger Fabric Functionalities.
- Hyperledger Fabric Model.
- Blockchain network.
- Identity.
- Membership.
- Peers.
- Smart Contracts and Chaincode.
- Ledger.
- The Ordering Service.
- Private data.
- Channel capabilities.
Additional reading materials
- Blogs by KC Tam
- What are the differences between Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Sawtooth?
- Hyperledger Fabric- The Most Popular Hyperledger Framework
Copyright Notice
Copyright (c) 2019. The Fabric-DevKit Authors. All rights reserved. SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0